(32) Draping an image over topography¶
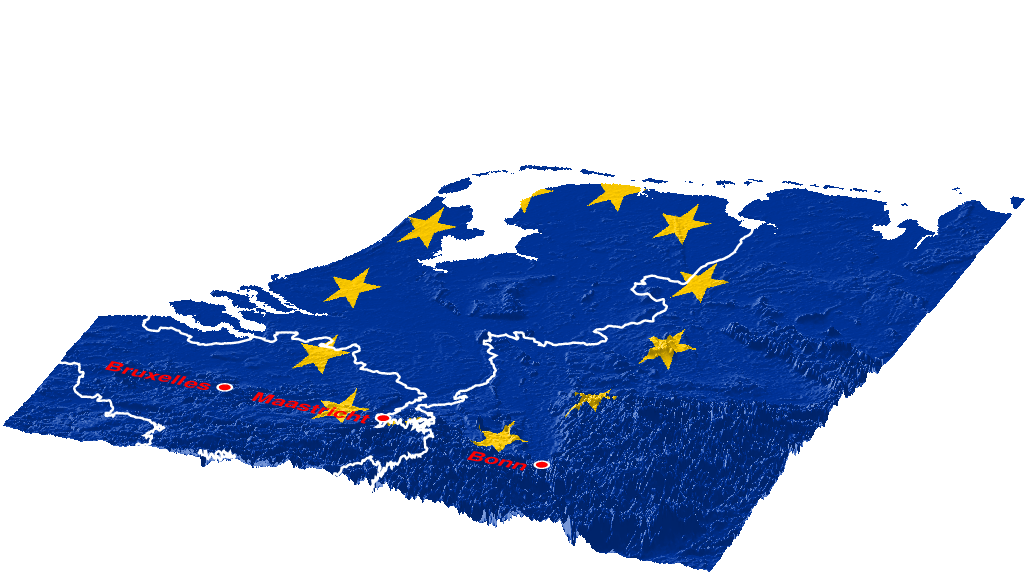
In some cases, it is nice to “drape” an arbitrary image over a topographic map. We have already seen how to use image to plot an image anywhere in out plot. But here are aim is different, we want to manipulate an image to shade it and plot it in 3-D over topography. This example was originally created by Stephan Eickschen for a flyer emphasizing the historical economical and cultural bond between Brussels, Maastricht and Bonn. Obviously, the flag of the European Union came to mind as a good “background”.
To avoid adding large files to this example, some steps have been already done. First we get the EU flag directly from the web and convert it to a grid with values ranging from 0 to 255, where the higher values will become yellow and the lower values blue. Then, grdedit adds the right grid dimension.
The second step is to reformat the GTOPO30 DEM file to a netCDF grid as well and then subsample it at the same pixels as the EU flag. We then illuminate the topography grid so we can use it later to emphasize the topography. The colors that we will use are those of the proper flag. Lower values will become blue and the upper values yellow.
The call the grdview plots a topography map of northwest continental Europe, with the flagged draped over it and with shading to show the little topography there is. coast is used in conjunction with grdtrack and plot3d to plot borders “at altitude”. Something similar is done at the end to plot some symbols and names for cities.
The script produces the plot in the Figure fig_ex32. Note that the PNG image of the flag can be downloaded directly in the call the grdconvert, but we have commented that out in the example. You will also see the grdcut command commented out because we did not want to store the 58 MB DEM file, whose location is mentioned in the script.
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# GMT EXAMPLE 32
#
# Purpose: Illustrate draping of an image over topography
# GMT modules: grdcut, grdedit, grdgradient, grdconvert, grdtrack, grdview
# GMT modules: coast, text, plot3d, makecpt
# Unix progs: cat, rm
# Credits: Original by Stephan Eickschen
#
gmt begin ex32
# Here we get and convert the flag of Europe directly from the web through grdconvert using
# GDAL support. We take into account the dimension of the flag (1000x667 pixels)
# for a ratio of 3x2.
# So simplify this example, we have stored the result, @euflag.nc in this directory.
Rflag=-R3/9/50/54
# gmt grdconvert \
# http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b7/Flag_of_Europe.svg/1000px-Flag_of_Europe.svg.png=gd \
# euflag.nc=ns
# gmt grdedit euflag.nc -fg $Rflag
# Now get the topography for the same area, mask out the oceans and store it as topo_32.nc.
gmt grdcut @earth_relief_30s_p $Rflag -Gtopo_32.nc=ns
gmt grdcut @earth_mask_30s_p $Rflag -Gmask_32.nc=ns
gmt grdmath topo_32.nc mask_32.nc 0 GT 0 NAN MUL = topo_32.nc
# The color map assigns "Reflex Blue" to the lower half of the 0-255 range and
# "Yellow" to the upper half.
gmt makecpt -C0/51/153,255/204/0 -T0,127,255 -N
# The next step is the plotting of the image.
# We use gmt grdview to plot the topography, euflag.nc to give the color, and illum.nc to give
# the shading.
Rplot=$Rflag/-10/790
gmt grdview topo_32.nc -JM13c $Rplot -C -G@euflag.nc -I+a0/270+ne0.6 -Qc -JZ1c -p157.5/30
# We now add borders. Because we have a 3-D plot, we want them to be plotted "at elevation".
# So we write out the borders, pipe them through grdtrack and then plot them with plot3d.
gmt coast $Rflag -Df -M -N1 | gmt grdtrack -Gtopo_32.nc -s+a | gmt plot3d $Rplot -JZ -p -W1p,white
# Finally, we add dots and names for three cities.
# Again, gmt grdtrack is used to put the dots "at elevation".
cat <<- EOF > cities.txt
05:41:27 50:51:05 Maastricht
04:21:00 50:51:00 Bruxelles
07:07:03 50:43:09 Bonn
EOF
gmt grdtrack -Gtopo_32.nc cities.txt | gmt plot3d $Rplot -JZ -p -Sc7p -W1p,white -Gred
gmt text -JZ -p -F+f12p,Helvetica-Bold,red+jRM -Dj0.1i/0 cities.txt
# cleanup
rm -f cities.txt topo_32.nc mask_32.nc
gmt end show
Draping an image over topography¶