gmtcolors
Explanation of color codes in GMT
Description
Colors can be specified in GMT as arguments to commands, generally as part of the -G or -W options to select polygon fill or outline pen. Colors are also used in color palette tables (CPTs) that help convert numerical values to colors.
GMT allows several ways to represent a color:
- Colorname
Specify one of the named colors below. All names are case-insensitive.
- R/G/B
Specify Red, Green, and Blue levels. Each value is separated by a slash and is in the range from 0 (dark) to 255 (light). This representation is used to color monitors.
- #RRGGBB
Specify Red, Green, and Blue levels in the way that it is done in HTML. Use two characters for each color channel, ranging from 00 (dark) to FF (light). Upper and lower case are allowed.
- Graylevel
For shades of gray, R = G = B, and only one number needs to be used. This representation is popular with black and white printers.
- H-S-V
Specify Hue in the range 0 to 360 (degrees), S saturation between 0 (not saturated) and 1 (fully saturated), and value V between 0 (dark) and 1 (light). Number are separated by hyphens. This representation can be helpful when hue varies a lot.
- C/M/Y/K
Specify Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and blacK. Each number is in the range from 0 (no paint) to 100 (maximum paint). This representation is used by most color printers.
List Of Colors
The chart below lists the 663 unique color names that can be used in GMT. For an interactive color picker, see GMT Color Picker.
Download PDF versions:
US tabloid size
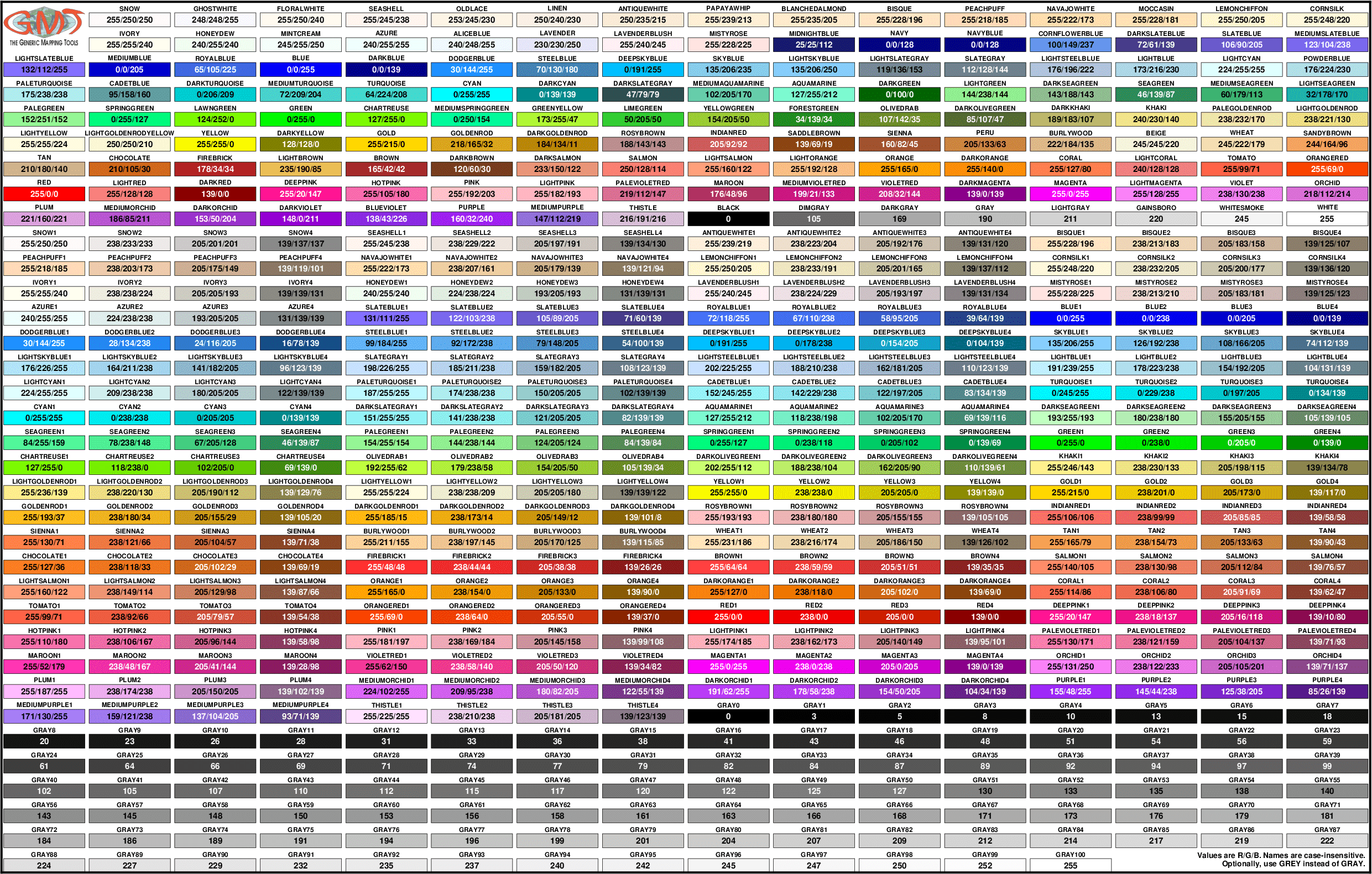
The 663 unique color names that can be used in GMT. Lower, upper, or mixed cases, as well as the british spelling of grey are allowed
Further Information
For more information on the use of color, read Chapter Color Systems and Artificial Illumination of the Technical Reference.
See Also
gmt.conf, logo, grdcontour, grdvector, grdview, basemap, coast, contour, histogram, image, legend, mask, rose, text, wiggle, plot, plot3d